10 Factors that are Propelling EDI Adoption and Growth

Understanding EDI’s Exponential Rise in the Age of Modernization and Obamacare
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) has long stood as an emblem of progress in the digital exchange of business documents between organizations. Its significance becomes increasingly vital within the healthcare sector, particularly when we look at claims data exchange. As the backbone of claims data and reporting, EDI’s influence has been pervasive, shaping the modern healthcare claims landscape and the myriad of businesses that support it. By offering streamlined operations, cost efficiencies, improved patient care and accountability, the benefits of EDI are multifaceted. There are a wide variety of reasons behind the soaring adoption of EDI and its symbiotic relationship with regulatory drivers such as the Affordable Care Act (ACA) often known as “Obamacare” and CMS reimbursement. EDI facilitates:
- Increased Efficiency and Expedited Speed: Gone are the days of manual claims processing with delays and redundancies and the need for vast numbers of human resources. EDI has automated these cumbersome processes, increased worker productivity, helped expedite claim resolution and offered the ability to channel resources effectively.
- Cost Reduction: The economic merits of EDI transcend mere paperwork reductions. From diminished errors leading to fewer reprocessed claims to less staff and staff focused on value-driven tasks, the savings stack up significantly.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: The global push for EDI arises from more government regulation and reimbursement reporting requirements along with the recognized benefits and subsequent standards set by governments and industry bodies. Adhering to these standards equates to smoother operations and streamlined data exchanges.
- Improved Accuracy and Minimized Errors: By minimizing human intervention there is a reduction in errors. EDI, with its standardized formats and validations, ensures precise data exchanges, which overall enhances accuracy.
- Advanced Data Analysis Capabilities: EDI makes structured data ready for immediate analysis, which enables swift insights into cost patterns, potential fraud, and more. This ultimately benefits patient care and operational efficiencies.
- Interoperability: EDI delivers interoperability by providing a unifying language in an industry with very diverse stakeholders. EDI bridges system disparities and ensures consistent and seamless data exchanges.
- Real-time Data Processing: As always, time is money. Market forces demand speed, and EDI delivers with real-time claims processing, which enhances cash flow and business transactions.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: The healthcare landscape is constantly evolving with new diseases, treatments and medical knowledge. The ability to add new codes into the EDI system allows healthcare providers and insurers to quickly adapt to these changes.
- Patient-Focused Care: At healthcare’s core lies the patient. EDI facilitates faster data processing, which leads to more insightful data-driven decisions and, ultimately, a higher quality of care.
- Environmental Benefits: Embracing the digital exchange of data results in lesser paper usage, which translates to clear environmental benefits.
How the ACA Accelerates EDI Adoption in Healthcare
Since its inception in 2010, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) has been a catalyst for significant changes in the U.S. healthcare system, particularly in augmenting the adoption of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI). The ACA’s influence is multifaceted and profound in several key areas.
One of the ACA’s primary impacts is transaction standardization. This mandate for uniformity is perfectly aligned with EDI’s capabilities, which simplify the data exchange process in the United States intricate multi-payer healthcare system. By standardizing transactions, EDI facilitates smoother and more efficient exchanges of healthcare information.
Administrative simplification is another crucial aspect of the ACA, aiming to streamline various administrative processes in healthcare. EDI stands out as an ideal solution in this regard. It ensures smooth, automated information exchanges, significantly reducing the administrative burden and enhancing operational efficiency.
Transparency and accountability are also heavily emphasized in the ACA. The Act demands robust reporting mechanisms to ensure transparent operations within healthcare organizations. EDI, with its specialization in precise and clear reporting, meets these requirements effectively, fostering greater accountability and transparency in healthcare services.
The expansion of coverage under the ACA has led to an increase in the insured population, consequently raising the volume of healthcare claims. This surge underscores the importance of EDI’s efficiency in handling high volumes of data and claims, making it an indispensable tool in the post-ACA healthcare landscape.
Timely operations are a focal point of the ACA, resonating with EDI’s capabilities for real-time data exchange. This alignment is crucial for the rapid submission and processing of healthcare data, directly impacting patient care and operational effectiveness.
The ACA has also mandated the use of Electronic Health Records (EHRs), which synergizes well with EDI. This synergy fosters an integrated electronic health data environment, streamlining patient information management and making healthcare delivery more effective.
The ACA’s drive to combat healthcare fraud has found a reliable ally in EDI. EDI’s efficient mechanisms for claim tracking and analysis scrutinize claims, thereby aiding in the prevention and detection of fraud.
Finally, the ACA employs a combination of penalties and incentives to ensure compliance and encourage best practices in healthcare. This approach further solidifies EDI’s role as a critical component in modern healthcare by incentivizing organizations to adopt these electronic systems.
EDI Stakeholders and Their Roles in Data Exchange
EDI, by definition, involves multiple participants in the data exchange process. Each of these participants plays a unique role, often defined by their position in the exchange chain or by the type of transactions they process.
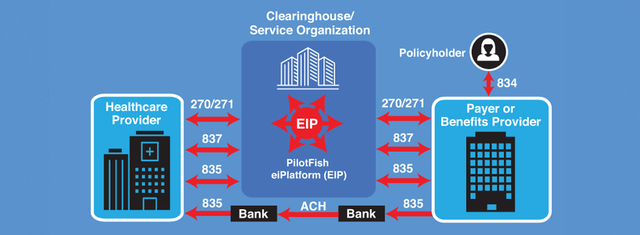
EDI 837/835 Workflow Example Between a Healthcare Provider and Payer or Benefits Provider
- Healthcare Service Providers: These include hospitals, clinics, and individual medical practitioners. They typically send out claim submissions, check eligibility and benefits requests, and receive claim status inquiries.
- Health Insurance Companies: These entities, like insurance companies, receive the claims from providers, process them and communicate back with acknowledgments, remittance advice or requests for additional information.
- EDI Clearinghouses: Acting as intermediaries, they receive EDI transmissions from providers, check them for accuracy, and forward them to the appropriate payers. They also help in converting non-standard data into EDI formats.
- Patient Engagement: While not directly involved in EDI processes, patients play an indirect role. Their personal, insurance, and medical data form the core of most EDI transactions. EDI streamlines their care by reducing administrative lag and ensuring data accuracy.
- Pharmacies: Pharmacies engage in EDI to check drug eligibility, get refill authorizations, and bill for medications.
- Transaction Used: EDI 278 Authorization and Referral transaction
- Transaction Used: NCPDP D.0 Pharmacy Claim Transaction
- Healthcare Vendors & Suppliers: For healthcare institutions that require equipment, medications, and other supplies, EDI transactions facilitate purchase orders, acknowledgments, and invoices.
- Banks and Financial Institutions: When it comes to electronic funds transfers, financial institutions leverage EDI for transactions related to payments and remittances.
- Transaction Used: EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice
Understanding the role of each participant is crucial as it helps streamline the processes, reduce errors and ensure efficient communication across the board. Each transaction is tailored to cater to the requirements of the specific data exchange, ensuring that the information is relevant, timely and actionable.
The EDI ecosystem in healthcare is a complex and integrated network – designed to make operations smoother, faster and more cost-effective. With the ACA amplifying the need for such exchanges and tools like PilotFish further simplifying EDI integrations, the healthcare industry stands poised for a future that is highly electronic, interconnected and patient-centric.
How PilotFish Helps to Support EDI Participants
PilotFish, recognized for its middleware solutions for over 20 years, has made a significant mark in the data integration space, particularly in the healthcare sector. When it comes to optimizing EDI standard utilization, PilotFish excels. Its enterprise integration platform provides a full suite of capabilities that are intuitive, optimized to enhance EDI standards and offer a highly scalable approach. Here’s how PilotFish helps users harness the power of EDI standards:
X12 EDI Interface Quick Tour with eiConsole
- Graphical Interface & No Coding: PilotFish offers a Graphical Integrated Development Environment (IDE). This eliminates the need for complex code, making it simpler for users to implement interfaces even if they lack a deep technical background.
- Template-Driven Approach: Users can capitalize on the ready-to-use templates and configurations for numerous EDI standards. This allows for swift integration setup, tailored to specific industry requirements.
- Data Transformation & Mapping: Using the eiConsole, PilotFish’s visual data mapper, users can seamlessly convert data from one format to another. For EDI, this means being able to translate EDI messages into other formats (like XML or JSON) and vice versa.
- Comprehensive Validation & Rigorous Testing: PilotFish provides validation tools that ensure the EDI messages adhere to the requisite standards. Moreover, the progressive testing functionality allows users to test and rectify interfaces throughout the development phase, ensuring accuracy.
- Extensive Support for EDI Standards: Whether it’s EDI X12 or any other prominent EDI standard, PilotFish’s middleware solutions are designed to handle them, ensuring broad compatibility and flexibility.
- Enhanced Connectivity: With PilotFish, users can seamlessly connect to any endpoint or system. Be it databases, applications, or platforms, the tool’s connectors, adapters and support for virtually any communications protocol you might encounter streamlines the EDI data integration process. (40+ Listeners, 30+ Transports and 140+ Processors built-in at no additional charge.)
- Scalability: As an organization grows, its data integration needs might expand. PilotFish is future-proof and architected to ensure that its solutions can scale to meet increasing demands, whether in terms of data volume or complexity.
- Ongoing Updates & Continuous Training: With the ever-evolving nature of standards and technologies, PilotFish remains committed to keeping its solutions updated. They offer training and support, ensuring users can adapt to and leverage any changes in EDI standards.
- Real-time Monitoring & Advanced Error Management: The platform offers real-time monitoring capabilities. Any issues with EDI data processing are flagged immediately, and the system can be configured to handle errors in specific ways, such as notifications, logs, or automated rectifications.
- End-to-End Integration Solution: PilotFish extends beyond mere data translation. Their suite covers the entire integration lifecycle, ensuring users can manage, monitor, validate data, test and maintain EDI data exchanges from a single platform.
PilotFish stands out as a solution provider for EDI integration. Its advanced features, combined with its architecture which ensures user-friendliness and adaptability, empower users to harness the full potential of EDI standards efficiently and effectively.
EDI: Empowering a Healthier Future through Digital Innovation
In conclusion, the ascent of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) in healthcare, energized by the Affordable Care Act (ACA) or “Obamacare”, marks a transformative era of enhanced efficiency and patient-centric care. EDI has become crucial in streamlining healthcare operations, ensuring compliance and fostering transparency, driving a significant shift towards optimized care delivery. Solutions like PilotFish are at the forefront, providing a robust, intuitive integration engine IDE (eiConsole) and platform (eiPlatform) that adapt and scale with the industry’s evolution. As a result, EDI’s strategic implementation is essential for a connected, efficient and forward-looking healthcare ecosystem.
If you have any additional questions or require further assistance, please don’t hesitate to contact our customer support team. Click on the button or jump into a chat.
X12, chartered by the American National Standards Institute for more than 35 years, develops and maintains EDI standards and XML schemas.

